
SPECTROSCOPY
Describe Spectroscopy:
Spectroscopy is the branch of science analysing the specrtrum energy in atoms or molecules. There are many different types of spectrocopy:
-
electromagnetic spectroscopy - The study electomagnetic radiation spectra given off or absorbed by atoms or molecules changing energy levels.
-
Atomic absorption spectroscopy
-
infra-red spectroscopy - The study of spectra showing infra-red radiation absorbed by atoms or molecules making them vibrate.
-
Mossbauer spectroscopy - Measures the absorption of gamma-rays by atoms bound in a solid as a function of gamma-ray energy.
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance - Measures the resonant absorption of RF radiation by nuclei in a strong magnetic field. Absorption peaks correspond to transitions in the nuclear spin states of the nuclei.
-
Electron spin resonance spectroscopy
-
Raman spectroscopy-The study of spectra caused by the scattering and change in frequency of light due to the transition between vibrational/rotational energy levels in molecules.
Uses of Spectroscopy in different industries:
Astronomy- helps the scientists find in depth information out about the temperature and build of the particular thing they are studying.
Forensics- helps in forensics because they have found out new ways and techniques of studying evidence. This includes being able to place a piece of evidence at the right angle of light and therefore that allows them to be able to see what they are looking for in the evidence.
Food Analysis- Spectroscopy makes it easy to see the quality of food and helps manufactures tell what is in it.
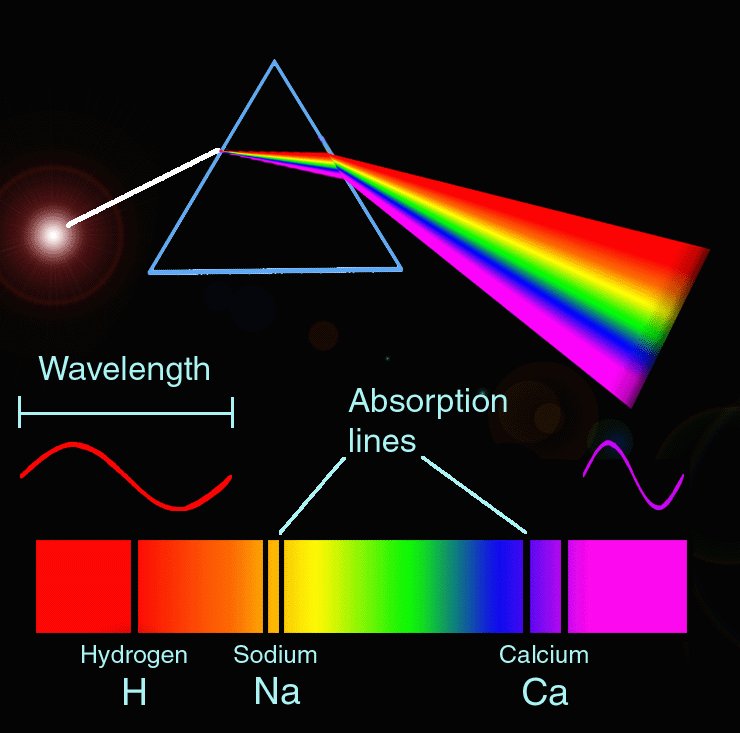
Spectroscopy in the universe:
Spectroscopy is used in the universe to look at stars, asteroids or any other objects that are in space or universe. They can tell this by measuring the waves length of light. Scientists know if something is coming closer becasue the wave lenths get shorter. It would also be in the blue spectrum. However when objects are moving away the waves become shoter and the spcrum becomes red.